Introduction
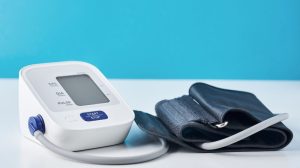
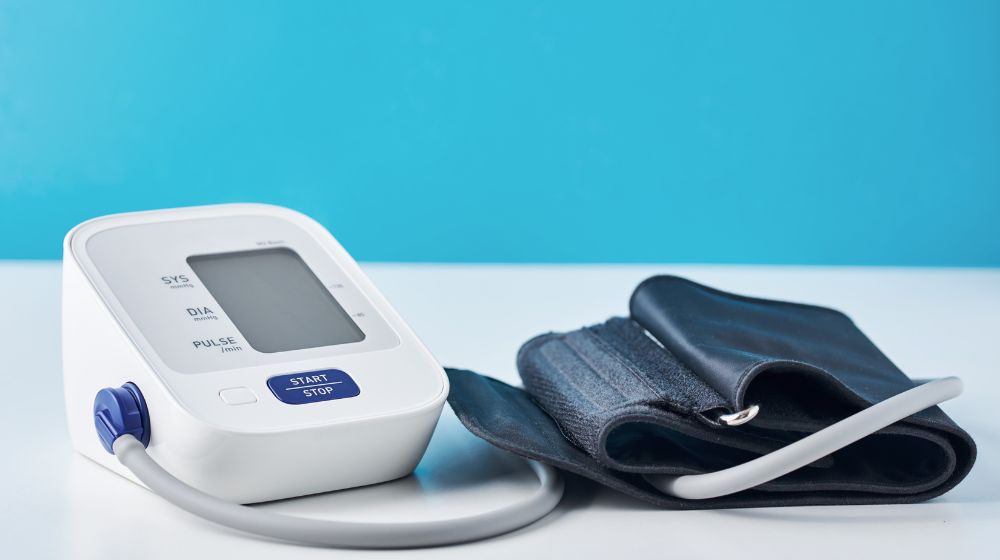
Digital blood pressure monitors have become essential tools for home healthcare, especially for individuals managing hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions. Their convenience, ease of use, and ability to provide quick readings make them a top choice for patients and caregivers alike. However, to ensure these devices provide accurate and reliable data, regular calibration and testing are necessary.
Inaccurate readings can lead to misdiagnosis, unnecessary medication adjustments, or missed signs of serious health conditions. This article explores how to properly calibrate a digital blood pressure monitor, how often to test its accuracy, and what signs to look for that might indicate your device needs attention.
Why Calibration Is Important for Digital Blood Pressure Monitors
Digital blood pressure monitors rely on sensitive electronic sensors and internal algorithms to detect and display blood pressure levels. Over time, these components may drift due to factors such as usage frequency, environmental conditions, or mechanical wear.
Calibration ensures that the systolic and diastolic readings stay within acceptable error margins compared to professional-grade equipment used in clinical settings. Without proper calibration, a monitor may consistently give results that are too high or too low, potentially leading to incorrect health decisions.
How Often Should A Digital Blood Pressure Monitor Be Calibrated?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to how often calibration should occur, but general recommendations include:
- Every one to two years, depending on usage and manufacturer guidance
- After noticeable discrepancies with clinical or manual readings
- Following a device drop or visible damage
- Before resuming use after long storage
Some manufacturers suggest more frequent calibration for devices used multiple times a day or in professional environments, such as nursing homes or clinics. Always consult your user manual for brand-specific recommendations.
Signs That Your Blood Pressure Monitor May Need Calibration
It’s not always easy to know when a monitor is out of calibration, but several warning signs can indicate a problem:
- Inconsistent readings when measured several times under the same conditions
- Differences of more than 10 mmHg between your monitor and a healthcare provider’s results
- Frequent error messages or abnormal inflation behavior
- The cuff inflates too much or too little
- The device is more than 2–3 years old and has never been checked
Recognizing these signs early can help you avoid relying on misleading data.
How to Test the Accuracy of A Digital Blood Pressure Monitor
Before attempting any calibration, it’s wise to first test the device’s accuracy. Here are a few simple yet effective methods:
1. Compare Readings at A Doctor’s Office
Bring your monitor to a scheduled doctor visit and compare its readings with those taken using a manual sphygmomanometer. Take multiple readings with both devices and assess whether the results consistently align within a 5–10 mmHg range.
2. Use A Blood Pressure Simulator
Medical supply companies or calibration professionals may use a blood pressure simulator, which mimics human arm blood pressure levels, to test a device’s measurement accuracy. While not typically available for home users, this method offers a high level of precision.
3. Dual Measurement Testing
Have two blood pressure monitors—your device and a clinically validated unit—connected in succession to take back-to-back readings. If there is a consistent deviation in results, your device may need calibration or replacement.
How to Calibrate A Digital Blood Pressure Monitor
Unlike analog equipment, digital blood pressure monitors cannot usually be calibrated at home by users. Calibration typically involves internal adjustments to electronic sensors and is performed by professionals or the manufacturer.
Manufacturer Calibration Services
Most major brands offer factory calibration services, where users send their devices to an authorized service center. The manufacturer will inspect, recalibrate, and verify performance based on ISO or ANSI standards. This is the most reliable method and is usually recommended every 1–2 years.
Third-Party Calibration Providers
Some certified biomedical equipment technicians or healthcare suppliers offer third-party calibration services. These professionals use certified pressure gauges and reference instruments to evaluate and adjust the device’s readings.
When Replacement Is the Better Option
In some cases, especially for low-cost models or devices older than five years, replacing the unit may be more cost-effective than recalibration. Modern monitors also offer better algorithms, memory functions, and accuracy standards.
Best Practices to Maintain Accuracy Between Calibrations
Even if your monitor is well-calibrated, user error and poor maintenance can still affect the results. Follow these best practices to ensure your device remains reliable:
- Use the correct cuff size for your arm. Too tight or too loose will skew results.
- Position the cuff properly—usually one inch above the elbow and at heart level.
- Sit still and upright for at least 5 minutes before measuring. Avoid talking or moving.
- Take multiple readings and average the results for better accuracy.
- Store the device in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight or humidity.
- Replace batteries regularly to avoid voltage fluctuations affecting performance.
Can You Calibrate a Blood Pressure Monitor at Home?
Technically, digital blood pressure monitors do not allow consumers to manually calibrate them. Some models may offer a zeroing function or allow basic system resets, but this does not equate to professional recalibration.
If you’re consistently seeing unusual readings, the best course of action is to:
- Verify results against a medical-grade device
- Contact customer support for troubleshooting or recalibration options
- Consider a professional evaluation if the device is critical for daily use
Conclusion
Accurate blood pressure monitoring is vital for managing cardiovascular health. Digital monitors offer convenience and ease of use, but their reliability depends on regular testing and occasional calibration. Understanding how and when to verify your device’s accuracy can help ensure that your readings are trustworthy and your health decisions well-informed.
Whether you’re using a monitor for routine home tracking or under a doctor’s guidance, staying proactive about accuracy protects both your peace of mind and your long-term wellness.